Feb 3 2021
Marimaca Copper Corp., a TSX-listed copper company, has announced the results of an induced polarization (IP) survey concluded at the Marimaca Copper Project. The IP survey has detected an elaborate chargeability anomaly below the flagship Marimaca Oxide Deposit (MOD) of the company.
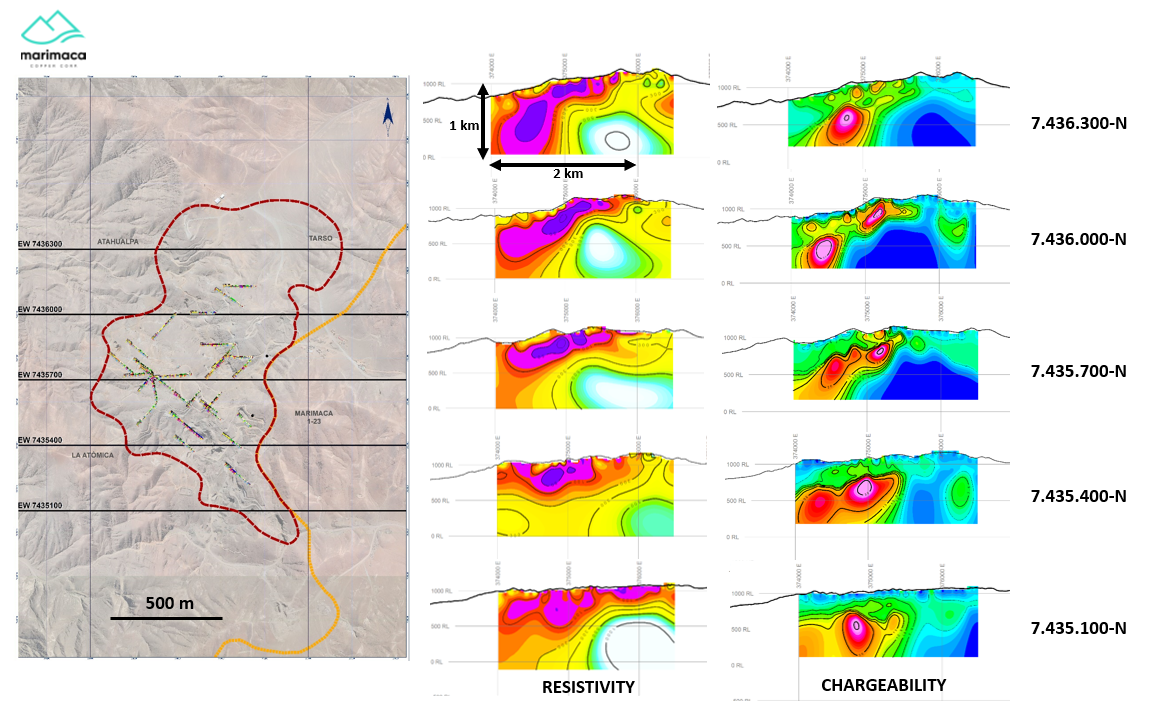 Location of IP Lines and Resistivity and Chargeability Sections. Drill holes with significant sulfide intersections shown on location map. Image Credit: Marimaca Copper Corp.
Location of IP Lines and Resistivity and Chargeability Sections. Drill holes with significant sulfide intersections shown on location map. Image Credit: Marimaca Copper Corp.
In 2002, Marimaca Copper concluded a Preliminary Economic Assessment (PEA) for the Marimaca Oxide Deposit, which emphasized its exclusive characteristics and demonstrates that the Marimaca Copper Project has the prospect to be among the lowest capital and operating cost copper projects during production, offering a post-tax NPV8 of US$524m utilizing a US$3.15/lb copper value.
The Preliminary Economic Assessment is believed to be preliminary in nature and comprises Inferred Mineral Resources. Geologically, these resources are regarded to be too speculative to have the economic considerations applied that would facilitate classification as Mineral Reserves.
It is not certain whether the conclusions within the Preliminary Economic Assessment will be achieved. The Preliminary Economic Assessment is based on the material assumptions defined in the previous announcement made by Marimaca Copper.
Highlights
- Widespread high chargeability anomaly was detected which indicated the extensive presence of sulfide mineralization below the Marimaca Oxide Deposit
- Survey results offer multiple targets for the forthcoming drilling campaign
- Survey results also offer more data about structural controls of mineralization and continue to add to the geological interpretation of Marimaca Oxide Deposit
- Surface geological mapping, as well as geochemical sampling at Cindy target, has been concluded and results are pending
- IP results for Cindy and Mercedes targets are anticipated shortly
We are very pleased with the results of the IP survey, which show a large, laterally extensive, chargeability anomaly beneath the Marimaca Oxide Deposit. This provides us with valuable data to inform drill hole targeting.
Sergio Rivera, VP Exploration, Marimaca Copper Corp.
“The IP has provided significant additional structural information, including highlighting the importance of the various cross-cutting fault structures for the mineralization at Marimaca. This has provided us with several areas of focus for drilling at the Marimaca Sulphide Target.”
We have also completed IP and geochemical sampling at our Cindy and Mercedes targets and are now assembling a considerable portfolio of targets which we believe could represent repetitions of Marimaca style mineralization, close to our flagship Marimaca Copper Project.
Sergio Rivera, VP Exploration, Marimaca Copper Corp.
“We expect 2021 to be a pivotal year for our Company, with numerous value creating opportunities, and we look forward to executing on our exploration strategy over the coming months,” Rivera added.
Overview of Induced Polarization Survey and Results
Marimaca Copper concluded an IP survey across the Marimaca Oxide Deposit with the goal of detecting sulfide mineralization areas related to, or close to, the Marimaca Oxide Deposit. The IP technique was chosen because of its high levels of resolution and deep penetration.
GRS Chile Ltda. completed the IP survey that involved five east-west lines on 300-m north-south spacing for a total of kilometers of 17.5 lines.
The resistivity low anomalies, that is, darker colors, match with an existing upper, supergene-altered, highly fractured, intrusive host rock, with the supergene oxide blanket accompanied by a few discrete anomalies.
Toward the east, the north-south striking, east-dipping nature of the primary fracture pattern, is maintained by a relatively uniform resistivity high (lighter colors), as shown in the above image.
The IP chargeability high anomaly demonstrated a wide, blanket-like, laterally extensive distribution, as indicated in the above image. The maximum values seem to coincide with the significant west-north-west trending fractures that are believed to be crucial controls of mineralization for the Marimaca Oxide Deposit.
It was observed that the chargeability anomaly is the most consistent and strongest in the southern part of the Marimaca Oxide Deposit, in which it was also seen to be highly coincident with the magnetic anomaly detected in the high-resolution drone-mounted magnetic survey.
From a geological standpoint, the north-south striking, east-dipping primary structure is denoted by low chargeability zones, whereas the upper limit of hanging wall alteration is clearly defined.
The magnetic anomaly demonstrated an excellent correlation between structural patterns and geology delineated by drilling. Magnetic susceptibility measurements made on drill specimens at the Marimaca Oxide Deposit confirmed a direct association between chalcopyrite and magnetite.
This was also confirmed by follow-up down hole magnetic susceptibility combined with Fe assays and Gamma-Ray surveys.
In plan view, 3D modeling of the copper sulfides intersected in drilling at the Marimaca Oxide Deposit reveals an apparent link with the north-west trending fault structures detected across the deposit, except for the central zone surrounding the Marimaca fault.
It was also believed that drilling operation conducted in other regions, which was concluded in topographical highs (as opposed to the Marimaca fault valley) could have been too shallow to have intersected prospective sulfide mineralization.